Robotic Process Automation
A Beginner’s Guide To
Robotic Process Automation
-
-
-
- Chapter 1: What is Robotic Process Automation?
- Chapter 2: Benefits of Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
- Chapter 3: How does RPA differ from BPM, BPA and other technologies?
- Chapter 4: Key features of Robotic Process Automation
- Chapter 5: Common RPA use cases
- Chapter 6: Who uses Robotic Process Automation?
- Chapter 7: How much does RPA cost?
- Chapter 8: Which factors should I consider when choosing an RPA solution?
-
-
Introduction to Robotic Transfer Automation
If you’re reading this page you’ve probably found or been introduced to the term Robotic Process Automation, or RPA, and want to find out more. Congratulations – you’re in the right place. It may be that you are intrigued about what it can do, or you have identified business processes that are manual. Either way you will learn about RPA here. And of course, if you don’t find out the answer your are looking for you can always ask us. To make sure you’re not wasting your time, let’s start by defining RPA. Then you can be sure the following information will be of use.
Chapter 1:
What is Robotic Process Automation?Robotic Process Automation, commonly known a RPA, is a software solution used to complete tasks that would ordinarily require a person.
RPA uses software robots—or agents—to streamline repeated tasks for both IT and business users. It can be installed on a PC, a physical server, or a virtual machine.
The robot interacts with systems the same way a human user does—clicking buttons, typing login credentials into a website, reading words off a PDF, and so on.
This can range from simple processes to improve personal productivity for individuals and teams, through business applications, to enterprise automation incorporating the whole infrastructure. As the technology matures, it’s increasingly becoming a more comprehensive enterprise automation solution. One that can interact with a GUI, but also one that provides deep integrations and sophisticated, enterprise-class features.
This shift in focus extends the benefits of Robotic Process Automation software from saving a few hours of a user’s time, to powering an enterprise-wide digital transformation.
There’s a variety of benefits of Robotic Process Automation for a business. Utilising its functionality can help an organisations reputation, as well as staff happiness and cost savings.
Employee satisfaction
Research tells us 90% of employees are burdened with boring repetitive tasks, which leads to dissatisfaction and wasted time. Automating these tasks frees them up to add more value to their organisation and their job satisfaction increases.
Save time
Automating manual processes can save businesses vast amounts of time. This frees up the workforce to focus on more important or even business-critical tasks. RPA solutions are easy to use for non-programmers, so less time is spent by IT developing and maintaining custom scripts.
Efficient and cost effective
The ability to do more with less keeps profits up without incurring costs. The business can operate more efficiently, which paves the way for business growth.
Accuracy
Human error is inevitable. By reducing repetitive manual processes, RPA eliminates errors, getting the task right first time. Data is more accurate, tasks are completed accurately and follow-on processes are less likely to encounter errors.
Resilient
RPA solutions are not affected by outside influences in the same way people are. This means processes can continue uninterrupted at times of staff sickness or if a workforce is reduced for other reasons. This can be an important aspect of business continuity and risk mitigation.
Visibility
RPA comes with reporting and visibility features, providing organisations with a single-pane-of-glass view of their data.
Adaptability
When requirements change, a robot can be reconfigured within minutes, as opposed to retraining employees which takes more time. It can also respond to changes – such as seasonal demand – more easily than people.
24/7
An RPA solution doesn’t need breaks and works nights, weekends and holidays. Data is available or processes completed more quickly, and employees can use it to add more value.

- Business Process Management (BPM) focuses on optimising business processes to improve operational agility and corporate performance. It is not a type of technology in itself.
- Business Process Automation (BPA) and robotic process automation are often used synonymously. RPA puts a larger focus on automation at the user interface level. Both BPA and RPA emphasise ease-of-use for non-programmers and interfaces with cloud and web services.
- Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) involves the contracting of specific business processes to a third-party service provider.
- Workload automation and job scheduling: Workload automation focuses on IT processes and deep application integrations, while robotic process automation specialises in the end-user and GUI automation. But there’s plenty of overlap. Ideally, an organisation would have RPA and IT job scheduling solutions working together, offering automation that spans the entire enterprise.
You should look out for the following features in an RPA solution:
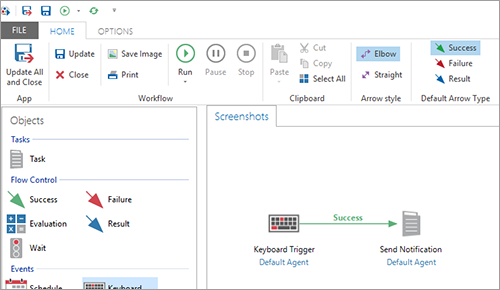
Easy drag and drop interface
Simple deployment
Full audit capabilities
HA and DR deployment support
Easily scalable
.png)
Comprehensive workflow support
Enterprise RPA
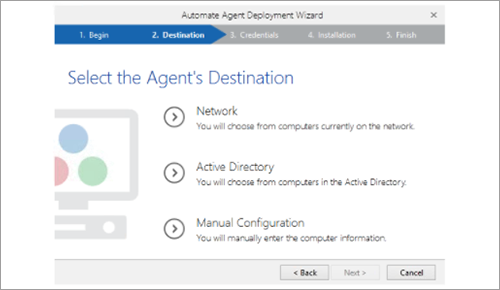
- Host, server and agents components. From the host, you can deploy agents to other machines on the network but you can control them from a central location.
- Workflow and workflow designer
- Centrally managed multi-machine execution
- Centralised repository
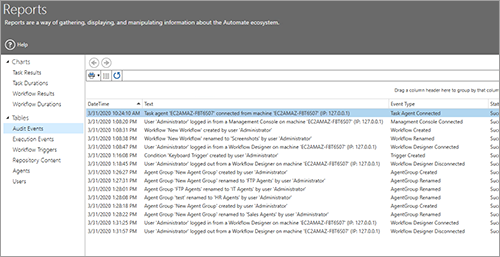
- Enhanced reporting and user dashboard
- Multiple user/administrative account
- Multiple user groups/group permissions
- SLA Management
- Workflow and task auditing
- Enhanced Security and Audit Platform
- *Operations Console
- Extended Agent Server
Interactivity
- Ideally these would be out-of-the-box API integrations:
- SOAP & REST/API
- FTP/SFTP/MFT
- OCR read
- Data transformation / manipulation
- FTP/ SFTP
- Web services
- Terminal emulation
- AWS/Azure
- Active Directory
- Webpage Integration
- Excel
- VMware
- MS SharePoint
- JMS
- Web services
Most businesses start using Robotic Process Automation to solve a specific problem or to optimise a single process – any repetitive task that a human does with keyboard and mouse. It is currently IT ‘back office’ but moving increasingly to use by end-users, who can directly invoke and monitor automated tasks.
Robotic process automation scales quite easily to streamline multi-machine processes and enhance team productivity.
Web browser task automation
RPA interacts with web browsers to do almost anything you can do on a website: Click links, select from a menu, type into a text box and more. There are three categories for building processes: browser automation, interactivity actions and input. Exchange rate management is a good example.
Data scraping and extraction
RPA data extraction, transformation and transport tools remove the need for tedious manual tasks or custom script writing. Data extraction can be used with web browsers, email, databases and with Excel, PDF, CSV, and OCR filetypes.
Managing user accounts
RPA simplifies managing user accounts. It can create, remove or modify Active Directory users and verify user information. It can deliver a range of change requests, such as resetting user passwords or migrating users from one organisational unit to another.
Report generation
Execute reports from Excel, Crystal Reports or other tools. RPA saves them in the right format, then emails a distribution list. It can perform direct queries and stored procedures from databases or applications (ERP, GL) and export results to Excel graph templates.
Automated file transfer process
Automate file operation on a schedule, based on any triggering event (eg: file arrives or is modified). RPA supports secure standards like SFTP and FTP over SSL, FXP for server-to-server transfers, file encryption using PGP, file compression and decompression and more.
Cloud automation
RPA can be deployed on premise or in the cloud and integrates with cloud technologies such as: Amazon Web Services (AWS), VMWare, JIT, Windows Azure and Jenkins. It integrates with any web service-based application and hosted business applications.
These case studies are just some examples of how different industries have leveraged the power of Robotic Process Automation.
Banking
A bank with 100 branches and 1000 employees previously did most processes manually. They now use RPA to update customer account information, onboard new employees, payroll and more. They also automated testing and validation of 300,000+ customer accounts for a core conversion to a new system. They have 75 software robots in production.

Public Sector
A public sector department needed to get key information from PDFs into a Microsoft Excel template. They would spend a significant amount of time manually extracting and transcribing the relevant data into Excel.
With RPA, they leverage Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to read and extract the necessary information from the PDFs and put it directly into Excel. The user-friendly interface is an intuitive way to instruct the bot to schedule tasks and take action. They recaptured valuable time and resources needed to drive their mission-critical work.

Insurance
Closing out each month’s claims was a long, manual process for this insurance company’s IT staff. Now with RPA, a process automatically starts and runs unattended throughout the night. It will send an email notification in the event of an application malfunction, giving peace of mind.
RPA also generates the reports for regulatory bodies, who may request them without notice. It integrates with existing applications, like Crystal Reports, the Infinity system and Microsoft Great Plains. This provides regulators with the information they request simply and quickly.
This faster, more accurate report creation saves multiple employees days of work per month.

Retail
This company processes and ships £250 million of food nationwide each year. The high volume of orders would tie up their staff with mundane repetitive tasks, like manually faxing customer order files to their warehouse.
With RPA customer order files are transferred automatically to their warehouse. Then RPA runs other essential processes like monitoring supply levels and making SQL updates to their database.
RPA reliably delivers the files on time, without any manual intervention or monitoring.

NHS/Healthcare industry
This medical institution relies on three main applications: an HR system, a time and attendance system and a staffing system. Being up-to-date and synced enables the business to allocate the right number of staff, operating efficiently while providing quality care.
Switching between applications was taking up so much time, so RPA now delivers the thousands of transfers between these applications. Instead of having to worry about staffing levels and not having the most accurate and up-to-date data, they can keep the focus on their patients.
This particular company cited their return on investment at 650%.

Logistics
This company automated all aspects of their logistics process, from monitoring stock levels, receiving orders, tracking, delivery notifications and customer invoicing, whilst integrating with third party suppliers where necessary.

Chapter 7:
How much does Robotic Process Automation cost?
RPA installed on a single desktop computer can start from £3000. The aim of this is to improve individual or team productivity. Then the price scales as you add functionality.
The next level of automation involves centralising control over enterprise applications. Modern enterprises employ a wide array of business software across every department in the organisation. Maximizing the ROI of those applications involves going beyond any basic built-in schedulers they have and integrating each application into an enterprise-wide workflow.
Lastly is automation for systems and infrastructure. Adding this type of solution allows businesses to enable DevOps, simplify compliance, monitor systems, and meet SLAs efficiently.
Chapter 8:
Which factors should I consider when choosing an RPA solution?Your requirements
This will largely depend on your business size. A desktop solution does just what it says – it operates on an individual’s computer. There is no central view and agents can’t be connected to work with each other.
Enterprise versions include host, server and agents components. This enables you to share automation programs across the infrastructure rather than having to build individually for each machine.
Intuitive and Accessible
A good RPA solution needs to be powerful enough for IT, but intuitive enough for business users. Look for a library of actions and activities to simplify bot development and a customised interface.
It should be mobilised and responsive. You need to view processes and run, stop, pause, resume, enable or disable any action from a mobile device. A web-based, responsive interface will allow users to take action immediately, from anywhere, if potential issues arise regarding workflows, missing files, etc.
Scalable
Streamlining individual processes can save a team hours every day, but a solution that can’t expand to other areas of the organisation or scale as the business grows provides a poor ROI. You may not need all these requirements now, but you what about in the future? So make sure you choose a solution that can move easily and cost-effectively from automating an individual user’s tasks to streamlining any high-volume processes in the organisation.
Contact us
We're always happy to help - however big or small your querySimply call or email us and one of our system integration specialists will be in touch to discuss your requirements or queries.
 0333 123 1240
0333 123 1240
 info@pro2colgroup.com
info@pro2colgroup.com
FAQ's
The basics
WHAT IS ROBOTIC PROCESS AUTOMATION?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a software solution used to complete tasks that would ordinarily require a person. RPA uses software robots—or agents—to interact with systems the same way a human user does. Eg: clicking buttons, typing login credentials into a website, reading words off a PDF, and so on. This can range from simple processes to improve personal productivity for individuals and teams, through business applications, to enterprise automation incorporating the whole infrastructure.
WHAT ARE THE FEATURES OF ROBOTIC PROCESS AUTOMATION (RPA)?
And RPA solution commonly includes:
- Easy drag and drop interface
- Simple deployment
- Easily scalable
- Full audit capabilities
- HA and DR deployment support
- Comprehensive workflow support – rules, variables, calculations, exception handling, triggers
- Extensive scheduling capabilities
- And more…
WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN RPA AND BPM?
BPM focuses on optimising business processes to improve operational agility and corporate performance. It is not a type of technology in itself. RPA is a software solution.