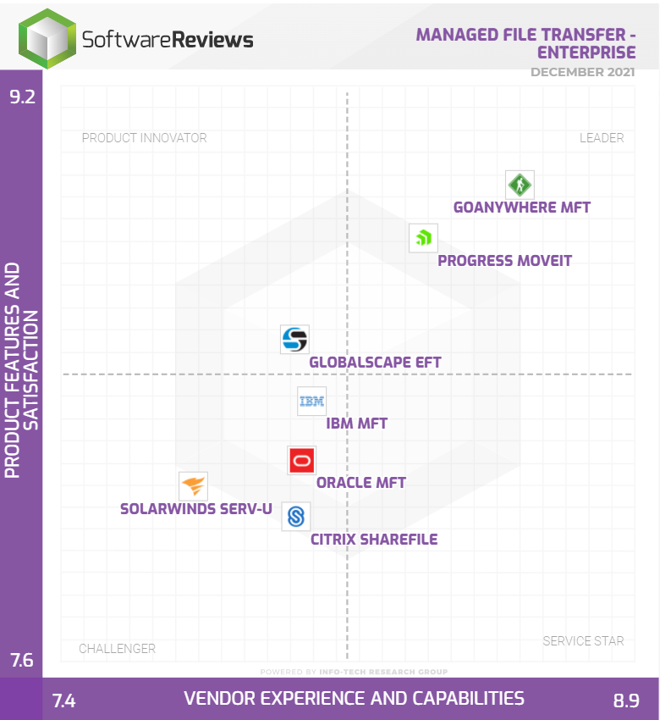
 As 2021 draws to a close, Software Reviews have released their latest Info-Tech MFT Data Quadrant. Regular readers of this blog will remember we highlighted concerns about the 2019 report – namely that several of the featured products weren’t actually managed file transfer (see our full 2019 review below ).So, what does the 2021 report look like, and is it a more accurate reflection of the marketplace?
As 2021 draws to a close, Software Reviews have released their latest Info-Tech MFT Data Quadrant. Regular readers of this blog will remember we highlighted concerns about the 2019 report – namely that several of the featured products weren’t actually managed file transfer (see our full 2019 review below ).So, what does the 2021 report look like, and is it a more accurate reflection of the marketplace?
System integration
System integration is defined as integrating existing, often disparate systems in order to improve performance. Data is transferred and transformed, uninterrupted, through the business process. Effectively the multiple disparate systems act as one co-ordinated system. This reduces operational costs and improves response times, with the overall IT infrastructure providing more value to the company.
-
-
-
- Chapter 1: What is system integration?
- Chapter 2: System integration solutions
- Chapter 3: Resources to help your system integration research
- Chapter 4: Who uses system integration solutions?
- Chapter 5: The latest system integration news and technical tips
- Chapter 6: Discuss system integration with an expert
-
-
Introduction to system integration
If you’re reading this page you have probably found or been introduced to the term ‘system integration’ and want to find out more. Congratulations – you’re in the right place. Perhaps you’re intrigued about what it can do, or you have identified disparate systems or applications that need to connect. Either way, here you will learn about system integration. You’ll find out how it can be achieved using different solutions and how they focus on different aspects. Of course, if you don’t find the answer you’re looking for you can always ask us. To make sure you’re not wasting your time, let’s start by defining system integration. Then you know the following information will be of use.

Chapter 1:
What is system integration?System integration technology connects disparate systems. This allows businesses to connect SaaS, cloud and on-premise applications, then integrate information through the business process. Essentially, data is transferred and transformed, uninterrupted, through a business process with the separate applications acting as one co-ordinated system.
There are multiple ways this is achieved, including the use of APIs (application programming interface). An API is the part of the application’s code that dictates how the sending and receiving of information takes place. By making it available, other applications can connect into it. The API allows the business to deliver data to the system, whereupon data transformation can translate it into a format and structure the target system can recognise and ingest.
EDI – or electronic data interchange – is another common form of integration. It is a computer-to-computer exchange of business documents. This exchange is based on a standard electronic format which allows business partners to interact.
Online retail is a great example of system integration. By integrating ordering, stock management and distribution systems, goods can be dispatched almost immediately. This opens up opportunities for great, customer-focused services like next day delivery or same day collection in store.
There are many benefits to system integration:
- The flow of data is unified through all applications.
- There are fewer manual data entry points, so the information stays clean and accurate (human intervention increases the risk of errors).
- Less time is spent on manual processing, allowing the business to operate more efficiently.
- The organisation has a complete picture of all interactions, so they can deliver an informed and personalised customer service.
- SLA monitoring is improved.
- Stringent security controls ensure compliance requirements are met and customers can be confident they are doing business with an organisation that protects their data.
There are technologies that focus solely on integrating other systems. Yet more and more of the applications themselves are being designed to connect with other new or legacy systems. Most of the time businesses find this addresses their integration requirements. Take Managed File Transfer, for example. MFT solutions deliver sophisticated integration capabilities, allowing businesses to move data securely, input it into its next end point effectively, and implement the follow on process efficiently.
Find out more by clicking on the solution types below.
Managed File Transfer
.png)
EDI
Automated File Transfer
Robotic Process Automation
Chapter 3:
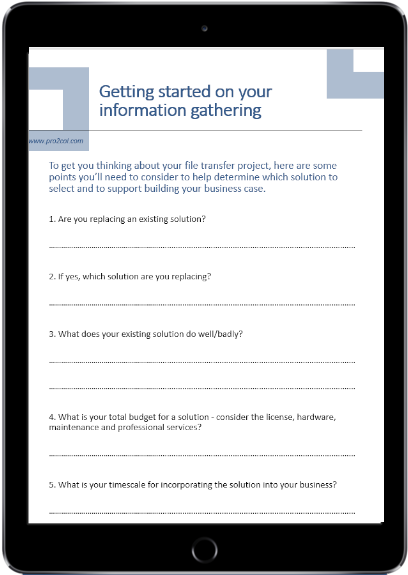
Resources to help your system integration researchStart your information gathering
Whether you need to integrate systems, transfer data securely or deliver automation, this is the ideal resource to get you started. Forty questions prompt you to identify current and future requirements.
Video: Managed File Transfer and digital transformation
This video explains how MFT integrates legacy systems and cloud-based applications (eg: Salesforce). It extracts the value from legacy systems, whilst enabling the use of new cloud-based systems.
White Paper: Digital transformation
File transfer and integration technology underpin digital transformation. This White Paper explains the essential role the two play in streamlining and securing your business processes.
These case studies are just some examples of how different industries have leveraged the power of system integration.
Wholesale, food and beverages
Using EDI to integrate ordering, stock management and distribution systems, goods can be dispatched almost immediately
A study by GS1 – who developed the most widely used supply chain standards – found that the grocery retail sector saves £650 million per year in costs by using EDI instead of manual, paper-based processes for its orders, invoices and despatch advices. Speed is the main benefit, with research citing a reduction in the processing time from 3-5 days, to a few minutes. Other benefits include: more accurate data, improved process efficiencies, cost savings and elimination of paper-based processing.
Other sectors leveraging the benefits of EDI include: Pubs, catering businesses, clothing retail, DIY, healthcare and public administration.

Public Sector
A local council used Managed File Transfer to move information to third-parties when it couldn’t securely connect via existing government gateways. Files were sensitive, such as reports concerning a member of the public, or a contractual negotiation with a supplier.
The solution was used by anyone wishing to send information to the council. Similar to a self-addressed envelope, a council employee could simply send an empty package to the third party, in which they place their documentation before pushing it back securely.

Insurance
Insurance regulators often request reports or audits with very little notice. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) integrates with the relevant applications, like Crystal Reports, the Infinity system and Microsoft Great Plains. RPA pulls the data, generates reports and provides regulators with the information they request simply and quickly. This faster, more accurate report creation saves multiple employees days of work per month.
RPA is also used to automate the closing out of each month’s claims, which saves IT staff a lot of time on what was previously a long, manual process.

Online Retail
By integrating ordering, stock management and distribution systems, the goods can be dispatched almost immediately. This opens up opportunities for great, customer-focused services like next day delivery or same day collection in store.
Data with fewer manual re-entry points will be more accurate, as human error is reduced. Costs associated with paper, printing, storage, postage and document retrieval are reduced. Goods and services can be delivered faster, which ultimately translates to growth and profit.

NHS and the healthcare industry
A medical company wanted to eliminate their reliance on a significant number of file integration protocols, which were owned by their former parent company. Rather than duplicate the existing complicated systems they installed Managed File Transfer to simplify and manage their automated and manual data transfers, whilst providing greater control and a more secure, reliable flow of data. This was particularly important for financial information such as invoices, orders and Bankers’ Automated Clearing Services (BACs) files. Managed File Transfer reduced their reliance on multiple solutions.

Managed File Transfer software comparison
Oct 14, 2021 | Blog , Automated File Transfer
 Start your Managed File Transfer software comparison. Answer a series of questions about your business requirements. We’ll compare how the different solutions meet your needs and make a free recommendation.
Start your Managed File Transfer software comparison. Answer a series of questions about your business requirements. We’ll compare how the different solutions meet your needs and make a free recommendation.
Solarwinds Serv-U MFT Server review
Sep 25, 2023 | Blog , Managed File Transfer , Pro2col
 We review Solarwinds Serv-U MFT Server and ask the question is it actually MFT and should it be seen as a leader in the market?
We review Solarwinds Serv-U MFT Server and ask the question is it actually MFT and should it be seen as a leader in the market?
Contact us
We're always happy to help - however big or small your querySimply call or email us and one of our system integration specialists will be in touch to discuss your requirements or queries.
 0333 123 1240
0333 123 1240
 info@pro2colgroup.com
info@pro2colgroup.com
FAQ's
The basics
What is system integration?
System integration is defined as integrating existing, often disparate systems in order to improve performance. Data is transferred and transformed, uninterrupted, through the business process. Effectively the multiple disparate applications act as one co-ordinated system.
What are the types of system integration?
• An API – or application programming interface – is the part of the application’s code that dictates how the sending and receiving of information takes place. By making it available, other applications can be connected into it.
• EDI – or electronic data interchange – is a common messaging structure that allows businesses to integrate with their partner/supplier systems.
What are system integration methods?
Systems are commonly integrated using APIs (application programming interface). APIs allows applications that would otherwise be separate to connect and interact. Essentially the API is the part of the application’s code that dictates how the sending and receiving of information takes place. By making it available, other applications can be connected into it.
What does system integration consists of?
System integration consists of connecting separate systems. This allows information to pass between those systems uninterrupted. If needed the data is transformed into a format the target system can ingest. This allows multiple disparate systems to act as one co-ordinated system.